

The author has 15 years of research experience in thin wall injection molding. Managing and producing more than 600 sets of thin-wall molds every year as a thin-wall injection molding engineer. Hoping that through this article, you can understand the knowledge of thin wall injection molding.
Thin-wall typically refers to small and medium-sized products with a wall thickness of 0.2mm-0.6mm (generally with a molding area within 0.1㎡). If the molding area increases, a 1mm wall thickness can also be considered thin-wall.
The following list outlines the definitions:
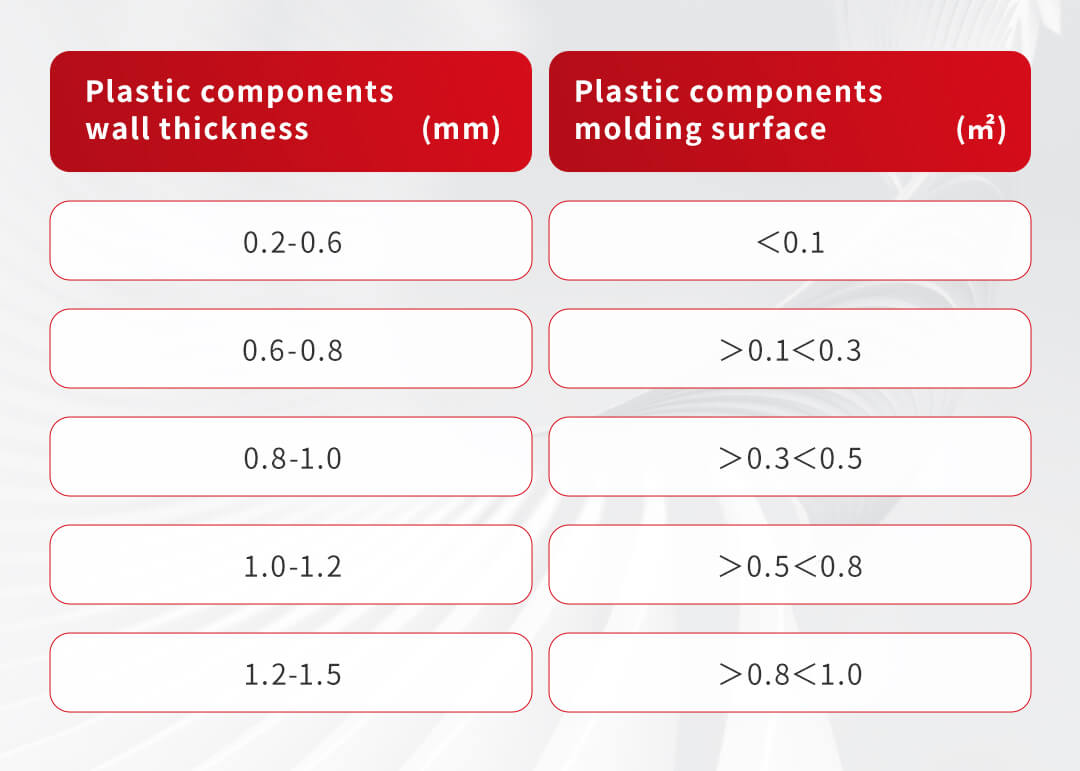
Remarks:
Above data is from Sino Mould recent 3 years various thin wall injection testing records.
Above data is based on DKM-HH series machine, with Injection Speed 300mm/s-500mm/s.(normally,the higher in-speed,the thiner wall can be molded).
The purpose of the above listing is to show that sometimes products with a 1.5mm thickness can also be considered thin-wall, depending on the size of the molding surface.
As we all know that injection molding involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold, which cools and solidifies to form the desired shape. The flow of the molten plastic in the mold cavity relies on the middle layer of the molten plastic, as the portions of the molten plastic in contact with the mold core and cavity sides solidify quickly.
Therefore, the principle of thin-wall injection molding differs significantly from thick-wall injection molding. Due to the thin walls, if the molten plastic flows slowly in the mold cavity, it will solidify quickly and the entire cavity can not be fully filled. Hence, it is necessary to fill the entire mold cavity quickly before the molten plastic cools and solidifies. This is why high-speed injection is crucial for thin-wall injection molding.
Thus, thin-wall injection molding can be equated to high-speed injection molding.
Comparison of Thick Wall Injection Molding and Thin Wall Injection Molding
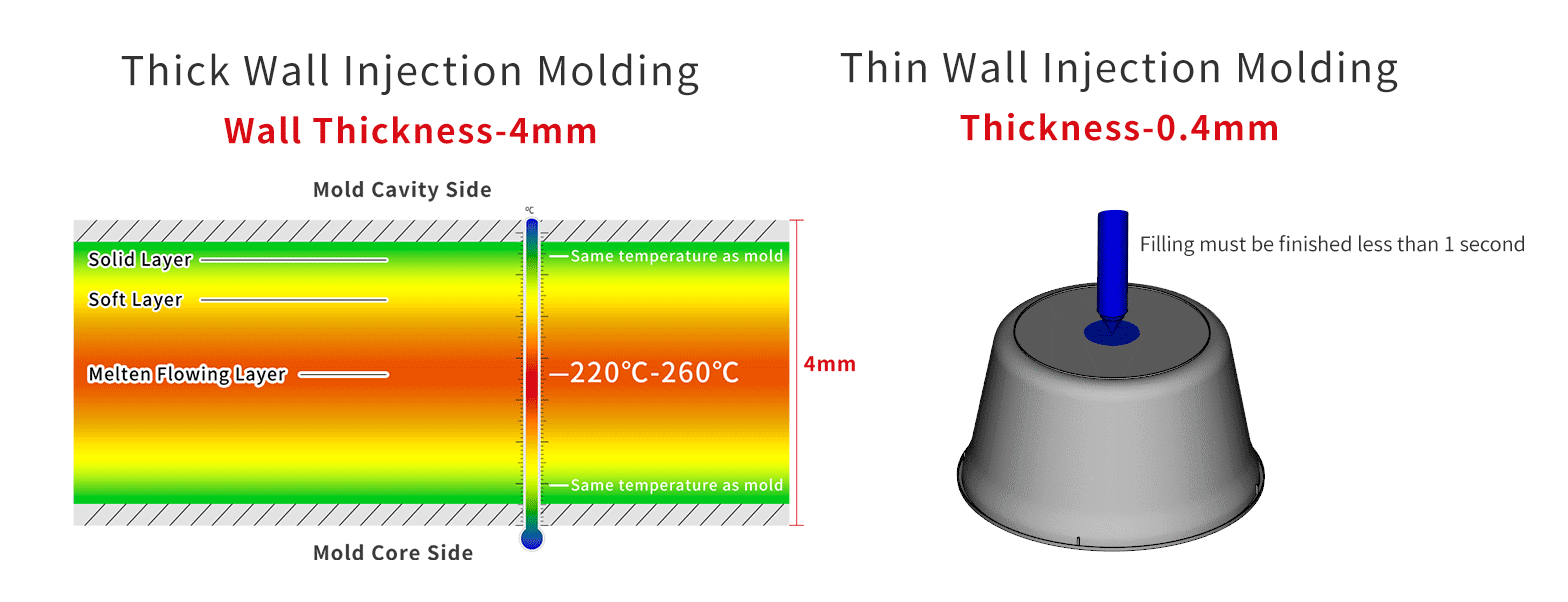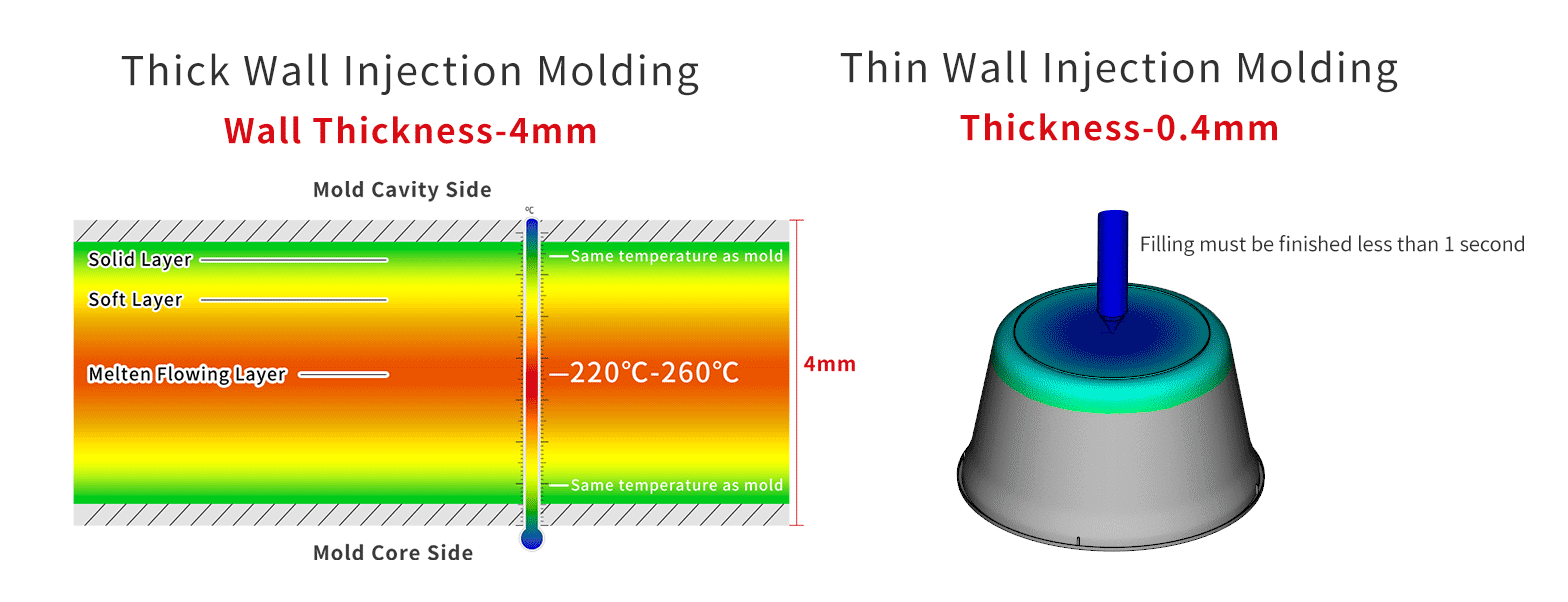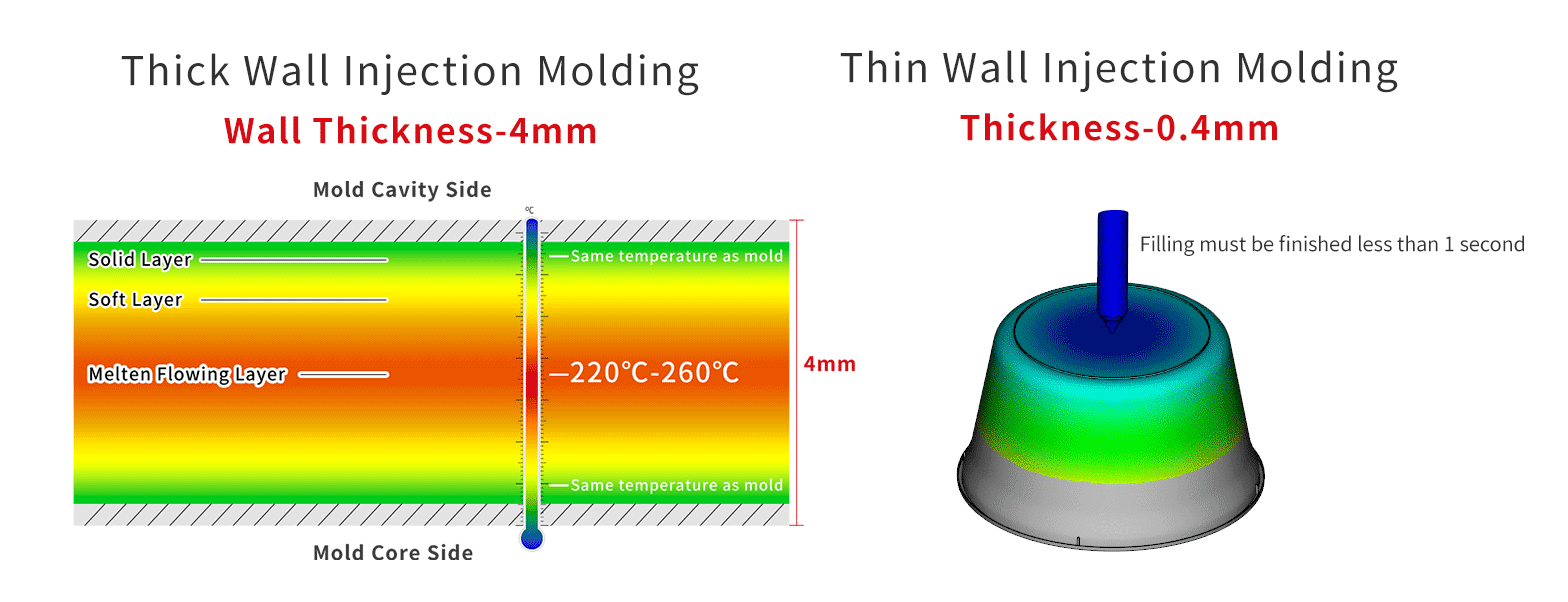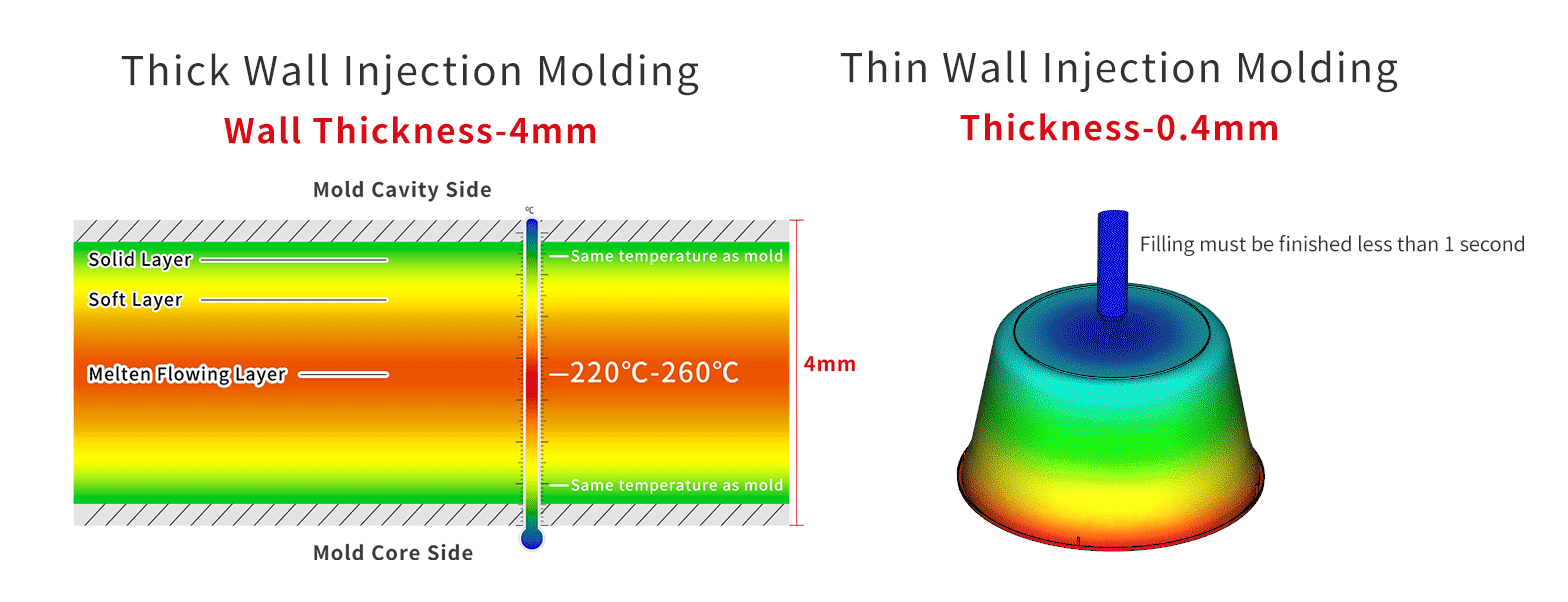
As shown in the figure, it is impossible to fill such a thin wall thickness through the slow flow of the central layer. It needs to be filled instantly.
The filling time of 0.4mm wall thickness product is only 0.2-0.3s.Therefore, high-speed injection is essential.
Designing and producing thin-wall injection molds require attention to four key points.
The filling time for thin-wall products is within 0.2s, meaning the material must fill the cavity uniformly in a very short time. Therefore, thin-wall molds have stringent requirements for hot runners. The hot runner in the mold design and manufacturing process must meet the following requirements:
Gate selection: Using a needle valve hot runner can employ larger diameter gates, speeding up the melt flow in the mold cavity and precisely controlling the injection pressure to maintain pressure balance.
Manifold balance: Ensuring the manifold flow path layout allows the melt to fill each cavity uniformly.
Temperature balance: Ensuring uniform temperature of the melt in the hot runner to avoid issues like cold material due to uneven heating.
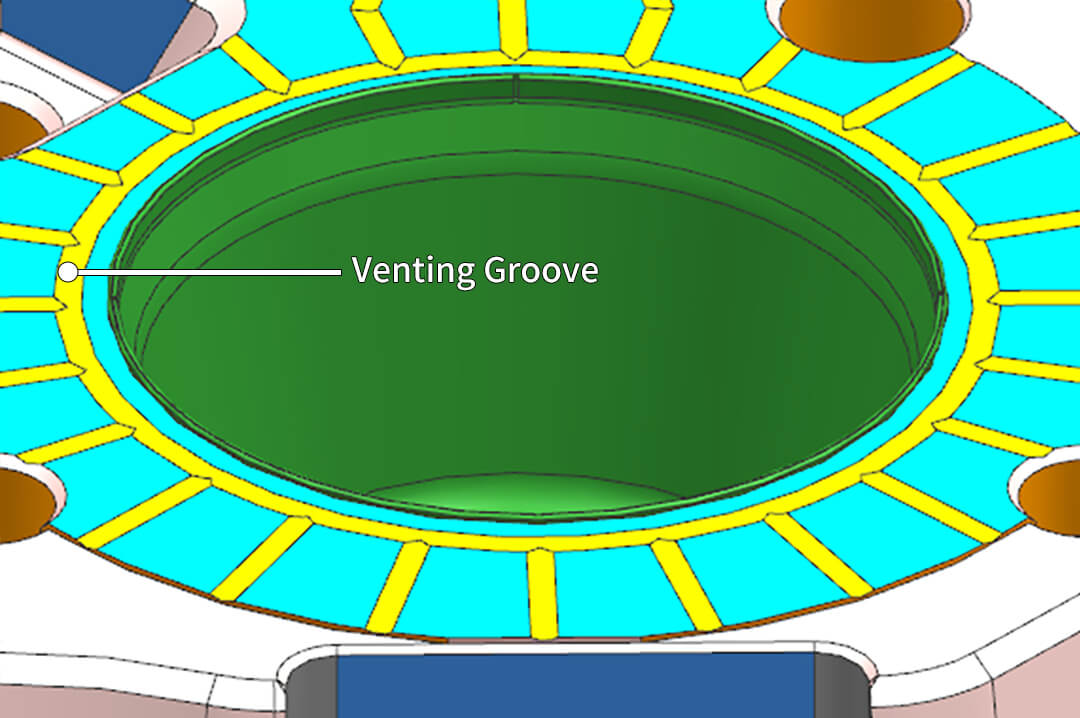
During high-speed thin-wall injection molding, the time for the plastic to fill the cavity is extremely short. To quickly expel the air and plastic volatiles inside the cavity, the mold must have good venting capabilities. Poor venting can lead to issues like incomplete filling, uneven filling, bubbles, or localized burn marks. Therefore, the placement and processing of mold vent grooves are crucial.
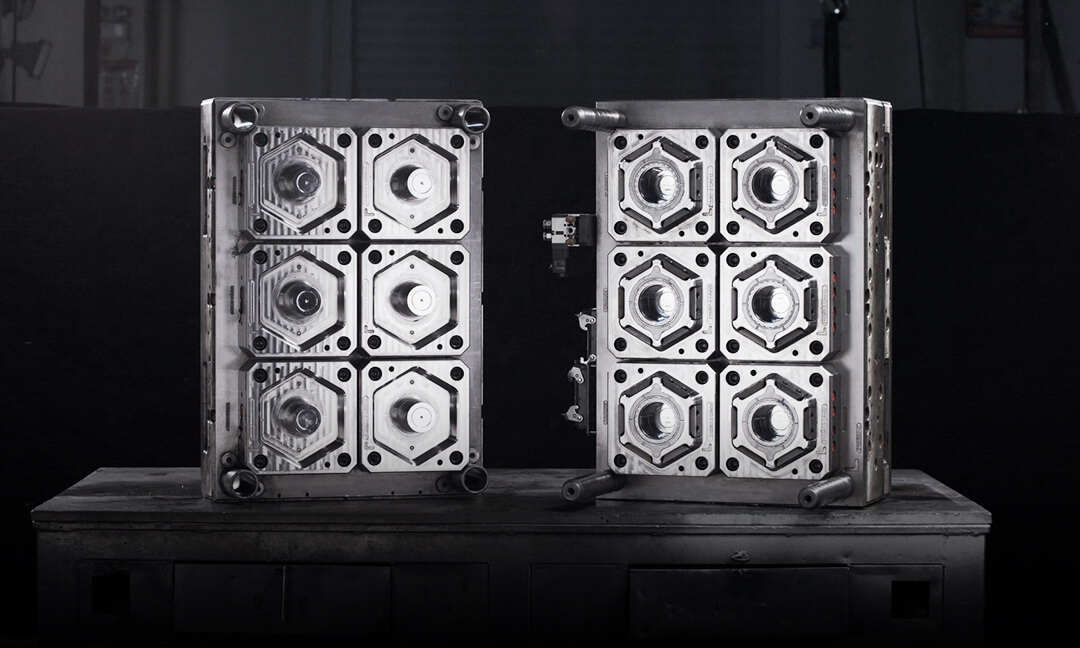
With thin-wall products having wall thicknesses less than 0.4mm, it is essential to ensure the processing precision of each mold component to distribute the melt uniformly within the mold cavity and avoid eccentricity issues. Thus, high-precision machining equipment must be selected for mold processing, with strict control over the cumulative tolerances of each component.
Thin-wall mold steel must possess the following properties:
High strength: The mold needs to withstand significant pressure and tensile forces, thus requiring high-strength steel.
High toughness: With very thin walls, the mold steel needs high toughness to prevent fractures during processing.
High hardness: The manufacture of thin-wall molds involves multiple processing and heat treatment steps, necessitating high hardness in the steel to ensure mold precision.
High wear resistance: Thin-wall molds must endure high-speed friction during use, requiring steel with high wear resistance.
Thin-wall injection molding requires filling the cavity instantaneously, necessitating injection speeds of 200 mm/s to 800 mm/s. The injection process is often completed within 0.2 seconds.
Since the injection volume in thin-wall molding is generally small, low repeatability precision in injection can lead to significant material volume discrepancies. Some injections may be short of material, while others may have flash, increasing the defect rate and reducing the efficiency of SOP mass production.
Thin-wall injection molding demands a very short molding cycle to maximize economic benefits. For instance, reducing the molding cycle of a product from 5 seconds to 4 seconds can increase production capacity by 20%, thereby enhancing profitability and market competitiveness. The speed of mold opening and closing directly impacts the molding cycle.
The shorter the cycle, the greater the profitability and competitiveness. Only by synchronizing actions such as injection, plasticizing, and mold opening and closing can the overall molding cycle be shortened. If these actions occur sequentially, the molding cycle will be long.
The energy consumption of injection molding machines includes the kinetic energy of each action and the thermal energy consumption of heating elements. The frequency of actions such as plasticizing, injection, mold opening, and ejection in thin-wall molding is much higher than that of conventional injection molding machines, potentially 3 to 10 times higher per unit time. Therefore, the energy efficiency of each action is crucial for profitability.
Regarding heating, we need to minimize heat loss as much as possible. For example, DKM's high-speed machines use internal heating to concentrate heat between the barrel and screw, ensuring that the external temperature remains below 50°C, thereby minimizing thermal energy waste.
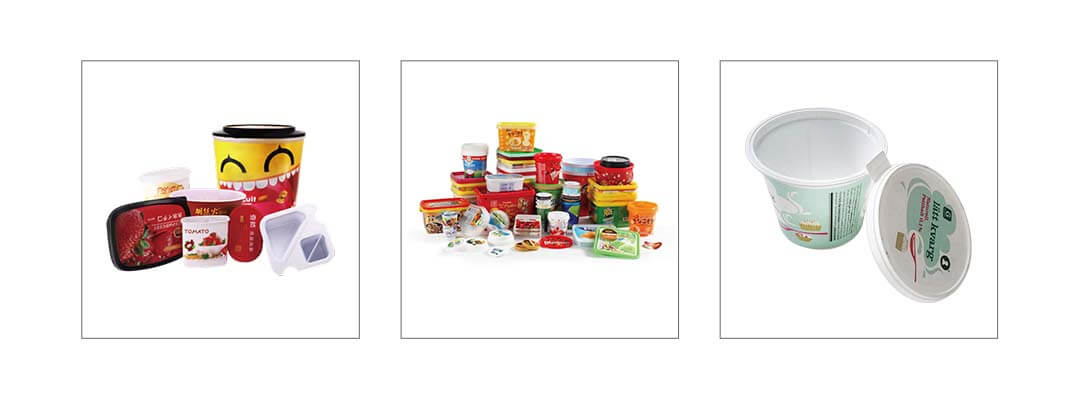
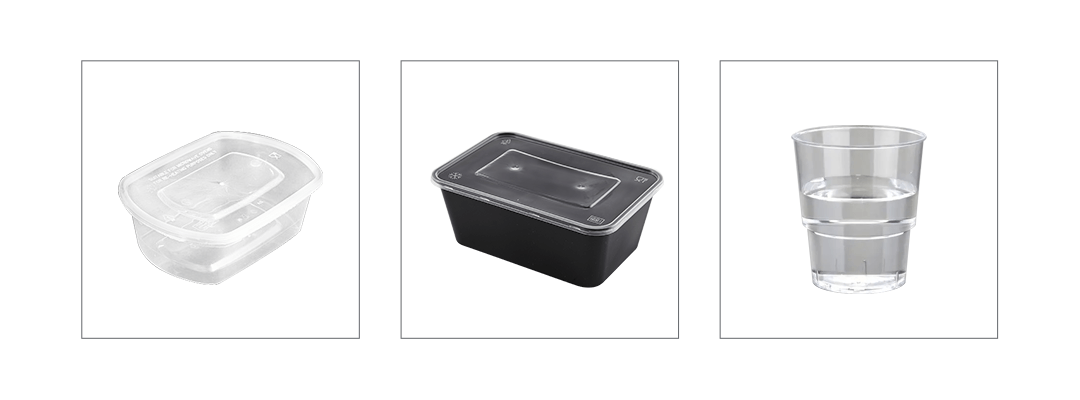
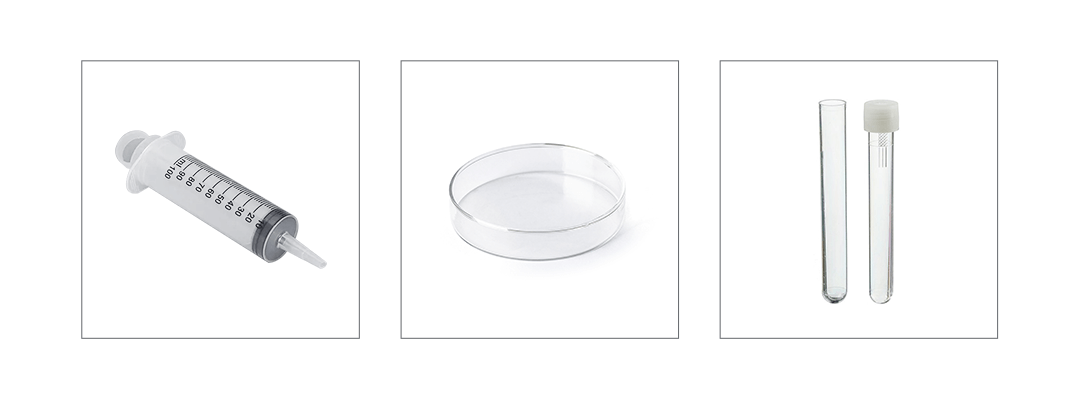
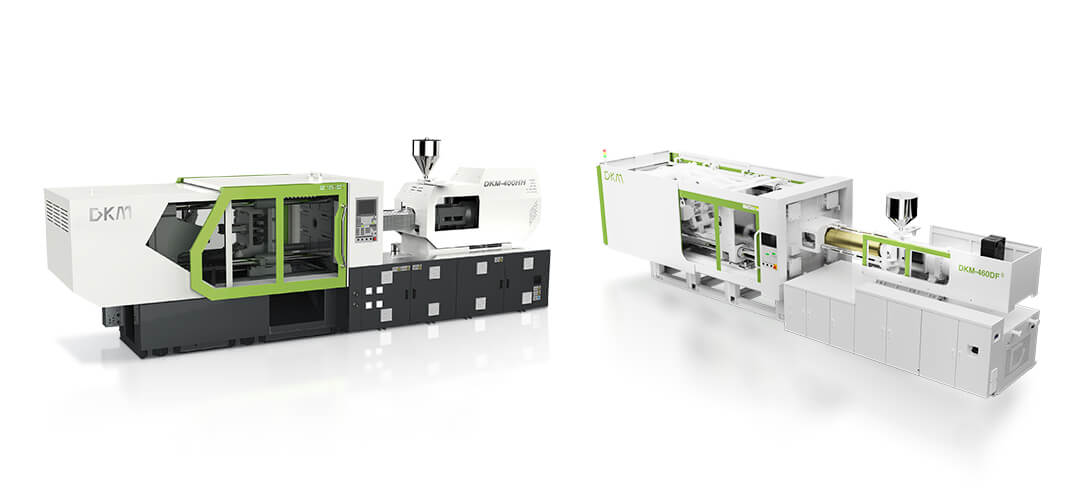




Thin-wall injection molding technology is a highly specialized manufacturing process, focusing on precise mold design, efficient injection machines, and optimized process control. This technology significantly reduces production cycles, lowers material costs, and improves production efficiency. It is widely used across various fields due to its efficiency, energy savings, and high quality, making it an essential part of modern manufacturing and continuously driving industry development and innovation.
Copyright © Sino Mould
Reproduction of this content without the author's permission is considered an infringement.