

This article popularizes blood collection tube molds, core for medical blood tube production. As a medical injection mold, it shapes tubes from PET/PP via injection molding. Key guidelines: pre-cleaning, accurate parameter matching, regular inspection. Standard use ensures tube quality and clinical testing accuracy.
Every time you have blood drawn at the hospital, the clean and standard blood collection tube you receive is inseparable from the "precision shaping" of the blood collection tube mold. As the core equipment for the production of medical blood collection tubes, the standardized use of the mold is directly related to the sealing performance and dimensional accuracy of the blood collection tube, which in turn affects the preservation of blood samples and the accuracy of testing. Today, let's spend some time talking about the core usage knowledge of blood collection tube molds.
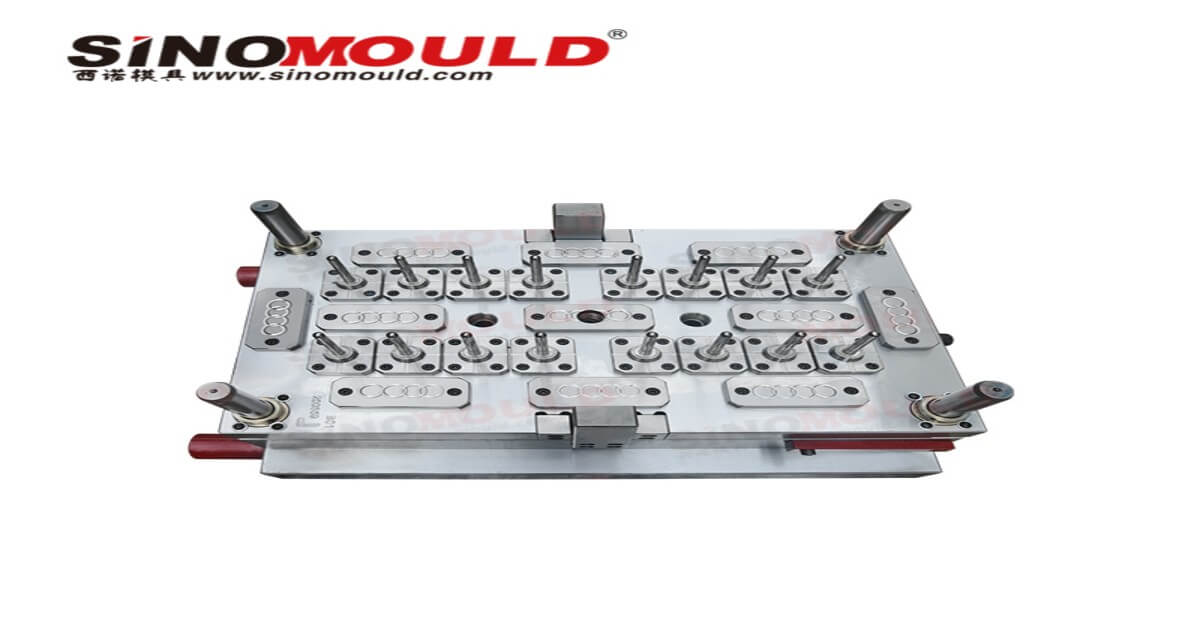
In essence, a blood collection tube mold is a "molding template". Through injection molding and other processes, it processes plastic raw materials (such as PET, PP) into blood collection tubes that meet medical standards. It determines the inner diameter, length, tube wall thickness of the blood collection tube, as well as key structures such as the sealing groove and scale line of the tube cap. It is the foundation for ensuring the versatility (compatible with blood collection needles and centrifuges) and safety of blood collection tubes.
1. Pre-cleaning: Before use, the mold cavity, core and sealing surface must be thoroughly cleaned to avoid residual plastic debris and dust. Otherwise, it will cause surface defects and poor sealing of the blood collection tube, affecting sample preservation. After cleaning, it should be dried to prevent moisture from mixing into the raw materials.
2. Parameter Matching: According to the material and specifications of the blood collection tube, accurately set the mold temperature, pressure, injection time and other parameters. For example, the mold temperature for PET materials should be controlled at 80-100℃. Excessively high pressure will easily lead to too thick tube walls, while excessively low pressure may cause material shortage and deformation.
3. Regular Inspection: During use, it is necessary to regularly check the mold for wear and deformation, especially the cavity and demolding mechanism. If wear occurs, it will cause dimensional deviation of the blood collection tube, and poor demolding may lead to tube damage, affecting production efficiency and product quality.
Simply put, the core of using blood collection tube molds is "cleaning, precision, and inspection"—none of which can be missing. Only by using the mold standardizedly can we produce blood collection tubes that meet medical standards, providing protection for clinical blood collection and testing.